Feudalism was a social system that developed in medieval Europe. It was based on the exchange of land for military service and loyalty. Under this system, nobles would grant land to vassals in return for their pledge of fealty (loyalty). This system resulted in the fragmentation of power, as vassals were often loyal to their lord rather than to the king.
The term “feudalism” is derived from the Latin word for fief, or land. In the 11th century, feudalism began to develop in Europe as a result of the decline of the Carolingian Empire. As nobles began to assert their power, they began to grant land to vassals in return for their loyalty.
Under feudalism, the king was still the supreme ruler, but his power was increasingly limited by the growing power of the nobles. This system allowed for the development of strong regional powers, which often led to conflict.
While feudalism began to decline in the late medieval period, it still has an impact on modern society. In many countries, the feudal system of land ownership continues to this day. Additionally, the idea of loyalty to one’s lord is still evident in many social and political relationships.
Feudalism was a form of loosely organized society based on the holding of lands in fief and on the resulting relations between lord and vassal. It flourished Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Word Feudalism is derived from the Latin word “feodum” or “feudum” which means fief.
What were the causes of feudalism?
Contents
After the fall of Rome, Europe’s condition was pathetic.
- No strong, central government to raise strong military, there was no protection from outside invaders.
- The feudal system emerged as a means to create order and stability. It provides a system of protection.
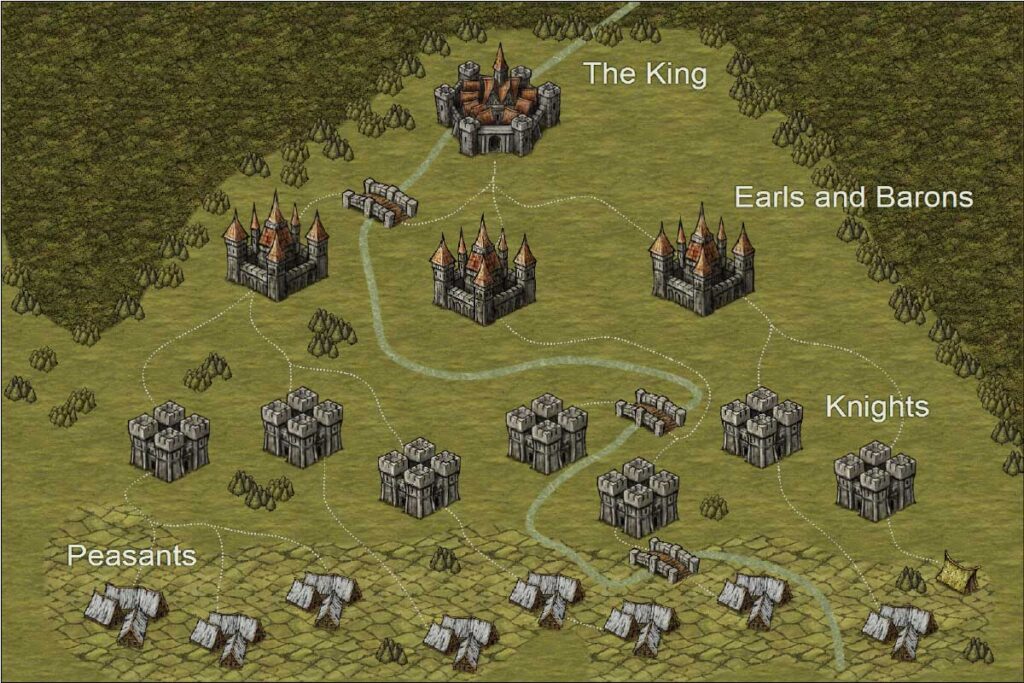
How was the feudalism pyramid of power?
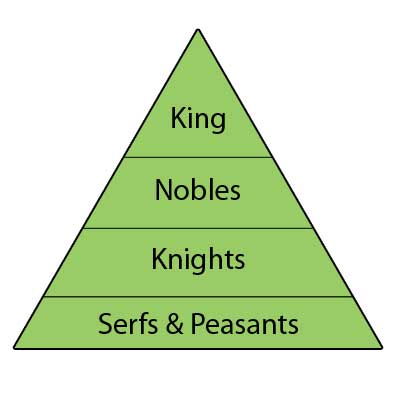
Serfs and Peasants
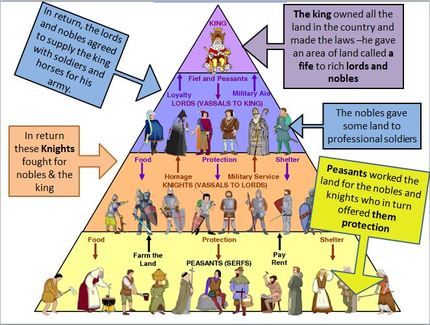
The lowest level of feudal society was made up of serfs and peasants. They were bound to the land. They were ruled by a lord. In return for their labour, they received protection from the lords/kings.
There were two groups of workers:
Serf and Peasants.
- Serfs were bound to the land by contract with the nobles. They had no freedom.
- Peasants or freeman were skilled workers who paid rent, they could leave the manor whenever they wished.
The next level of feudal society was made up of knights. They became soldiers for the king. They did military service. In return for their loyalty, they received land and protection.
The next level of feudal society was made up of nobles. They were the owners of the land given by the king in exchange for a pledge of loyalty.
Next and foremost level of feudal society was made up of king. He was the highest ruler of the land. Everyone owed loyalty to the king.
What were the effects of feudalism?
- Nobles became responsible for the protection of their serfs.
- The manor became agricultural estate operated by the king and worked by the peasants and serfs who sustained the land and drove the economy.
- Peasants were bound to pay to the king as a share of everything they produced.
Feudal land tenure, system by which land was held by tenants from lords. It developed in France and in medieval England. the king was lord paramount with numerous levels of lesser lords down to the occupying tenant.
What were the reasons for the decline of Feudalism?
How did feudalism end in the middle ages?
The crusades
Crusades were a series of religious wars. During the crusades, a large number of feudal lords lost their lives which gave a series set back to the feudal system. Some of the feudal lords who returned alive from the crusades were forced to sell charter of liberties to towns which they once controlled. As a result, a larger number of self attained freedom.
The Hundred year’s war
This was a series of battles between England and France from 1337 to 1453.
- People were loyal to their nation instead of their lords.
- Foot soldiers became more important as canons and longbows came into play. Knights and castles proved to be less efficient than the foot soldiers.
- Many people were killed during the war and those who were left demanded more rights and money.

The Black Death
The scarcity of labour force in Europe as a result of Black Death which took a heavy toll of life in Europe, enhanced the bargaining powers of the serfs and rendered feudal system.
Development in Trade and Commerce
The liberation of the serfs due to enormous growth in trade and commerce contributed to the decline of feudalism. With the growth of trade and commerce, a number of new cities and towns grew which provided new opportunities to work. The serfs got an opportunity to free themselves of the feudal lords by taking up work in the new towns.
Problems with knights
Feudalism was a way to provide protection and security quickly, throughout the Middle Ages the knight’s armour got heavier and more effective. On horseback, the medieval knights were a devastating weapon. On the foot, the weight of the armour between 20-40kg which made it difficult to move.
Legacy of Feudalism
- Loyalty and honour remain strong in European armies.
- Class structures still in existence in some countries.
- Surnames or family names- families took their names from their jobs, such as Baker, Cook, Taylor and Carpenter.
- Structures still remaining- Church, castles etc.
- Institutions still remain strong- Catholic Church.
Also read Feudalism in Germany, Feudalism in England