The Anglo-Saxons and the Vikings had left a major mark in the history of Britain that lasted over a thousand years. During this time, Roman Britain has undergone massive changes both in culture, religion, languages, and lifestyle of people. Do read what is anglo saxon?
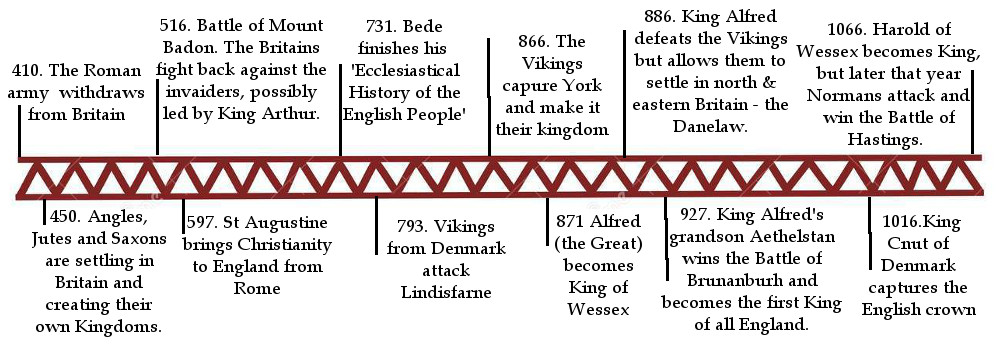
Since 360 AD Roman Britain has faced numerous invasions. They have been plundered by the Pics and Scots of Scotland, the Anglo-Saxons during the 5th century and lastly the Vikings in the late 7th century.
The continues raids and invasions created major shifts in the map of the country and also the religious and cultural beliefs of people.
Who came first Anglo-Saxons or Vikings?
The Romans left Britain in AD 410 leaving the country defenseless against foreign invaders. It was during this time in the 5th century that the Anglo-Saxons invaded England. However, the Romanized Britons tried their best to defend their lands and safeguard their culture from the new invaders.
The period in which the Anglo-Saxons ruled is often referred to as “Dark Ages” probably due to lack of proper written records of the Anglo-Saxon era.
The Anglo-Saxons were mainly from Northern Germany, Scandinavia, and Denmark. They were fierce warriors and ruthless as described by early Christian monks in their writings.
The Romans often deployed the Saxon warriors for mercenary services to defend the boundaries of England. But after the Romans left, the fearsome warriors raided all of England and mercilessly rampaged and killed men, women, and children.
Adomnan, a British monk suggested the “Law of the Innocents”, but the Saxons had no understanding of such laws and rejected it altogether.
After the Anglo-Saxon invasion, the seven Kingdoms were established; Northumbria, Kent, Sussex, Wessex, Essex, East Anglia, and Mercia.
All these kingdoms had independent rulers but shared similar culture and languages and amalgamated for a common cause.
Earlier, Britain was occupied by the Celtic people who worshipped Pagan gods and goddesses and gradually they shifted to Christianity towards the end of the century. Slowly the land of the Anglo-Saxons or “Angle-land” came to be known as England.
The Vikings came to England during the 7th century when the Anglo-Saxons were still in power. The first recorded Viking raid in England was in 793 AD.

The Vikings in England
Vikings were Nordic people who belonged to parts of Scandinavia, Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. The word Viking is derived from an old Norse word meaning “a pirate raid”.
The Vikings were, in fact, pirates and looted and raided the coasts of England during the late 8th century. They slaughtered people and rampaged monasteries and villages.
Their first attack was on 793 on the Monastery of Lindisfarne. The event was a significant landmark on history which was followed by continuous raids on the coastal villages and monasteries. They mainly targeted the churches and monasteries and looted them for their wealth.
In 865 AD the Heathen Danes arrived in East Anglia and within the next 9 years, they have succeeded to establish the Viking empire in England.
The Anglo-Saxons were not united and it was easy for the Vikings to defeat the individual rulers of Northumbria, East Anglia and some parts of Mercia. In 866, York or modern-day Yorkshire became the capital of the Viking empire.
Anglo-Saxons Vs Vikings
The Saxons were more civilized than the Vikings. It was King Alfred the Great of Wessex who finally defeated the Vikings at the Battle of Edington in 878. King Alfred took over more lands from the Vikings and ultimately in 886 he took over London.
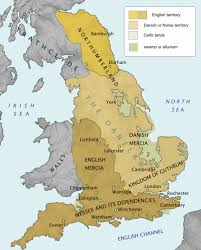
He established a new treaty with the Viking leader Guthrum whereby England was now partitioned between the Vikings and the English.
The Viking empire was known as the Danelaw and was subjected to Danish laws. Athelstan, King Alfred’s grandson became the new King of England.
Athelstan defeated the Vikings at the Battle of Brunanburh in 937 and Danelaw also came under the rule of England.
The Viking influence has not died yet and England witnessed several other Viking Kings, the greatest of them being King Cnut, the Danish King of England.
The final blow to the Viking rule came in 1066 AD when the last Viking King Harald Hardada was defeated by English King Harold Godwinson at Stamford Bridge near York.
However, this victory did not last long and on 14th October 1066, Harold of England was defeated by King William of Normandy in the great Battle of Hastings which marked the end of both Anglo-Saxon and Viking rule in England.

