In Europe, the society was based on social status and prestige. The way they dress, it reflects on their status. Clothing styles were heavily dependent on existing cultural traditions, social status and availability of raw materials. Maintenance of dress was also an important part which existed on the medieval era.
Raw material used in medieval clothing
Contents
Wool
In the middle ages, wool was by far the most common textile used in making cloth. Wool comes from animals such as sheep, camel and goats. Sheep were the most common source for wool in medieval Europe.
Linen
Linen is one of the first fibers that people made into string and cloth. Linen made from flax plant. Flax is a tall, red-like plant with long fibers which make it easy to spin into thread. It was used by all the classes. Fine linen was used for the veils and wimples of ladies, undergarment and household furnishing.
Silk
Europeans regarded silk as an extremely luxurious fibre. It had a great value. Silk has unique features; it is shiny, soft, light and resistant. It destined to become a status for wealthy families.
Leather
In the middle ages leather was used for belts, armour, furniture etc. leather could be dyed, painted for ornamentation.
Fur
Fur is a fashion phenomenon flourished in Europe. Fur clothing is not only soft, warm and durable but has often been a sign of wealth and rank in society. It was worn by nobleman on cloaks, hats and tunics.
Clothing
Clothing of Kings
European kings were inspired by the clothing of Byzantine Empire. They copied many of its style. They wore long tunics made of silk and embroidered with gold thread. Purple color was reserved for the clothing of the kings. Long wide T-shaped tunics were often worn in the ceremonies.
When kings had to attend his council, he used to change his dress; he used to wear dress made of silk, fur and jewels.
For hunting, king’s dress was simple and practical. They wore shorter cloaks, tunics, shirts and mail.
The most important part of medieval kings clothing was his crown which really showed off his wealth and status.

Clothing of the Churches
The Bishops, Priests and Archbishops were quite important in the middle ages. They were seldom wealthy.
Priests, Bishops and Archbishops wore special robes called Vestment for ceremonies; priest would also wear capes called Chasubles whereas the bishops and archbishops wore tall, pointed hats called Mitres and carried long hooked staffs to brandish their significance.
Pope was the powerful leader of the Church and being this he had to dress ornately. Pope of middle ages would dress primarily on red and white color, which indicates purity and supremacy.
He would wear red stockings and shoes under a white linen robe, with a red or white cloak named a papal mantle on the top, during ceremonies the pope would wear a crown and a small red cap called biretum as well.

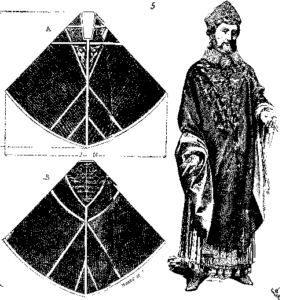
Clothing of the knights
Knights Suit of Armor were a series of garments, chain, and iron plate. The pieces of a Knights Suit of Armor covered the most vulnerable parts of a knight’s body.
His coat was emblazoned with the coat of arms in order to identify the knight in the battle. A person’s social status was determined by the head-dress or hat. The cap was made of velvet for persons of rank. Knights were forbidden to wear ring.

Clothing of Merchants
Merchants wore a coat above their knees. The coat would be of a bright color. They wore shoes with long tips.

Clothing of Monks and Nuns
Monks and nuns lives are dedicated to prayers. They wore open sided no top of habits. Habits are long tunics. Nuns always wore veils to cover their heads.


Peasants clothing
The cloths of the peasants were basic. Their clothing consisted of linen breeches, capes made of coarse wool and short tight tunics. At the waist the tunics were held by a belt in which a knife was kept. In terms of footwear, they wore small, pointed or tougher boots for working.
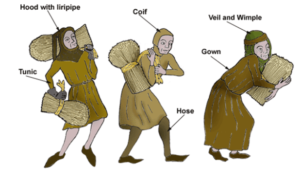
Women’s clothing
Queens and noblewomen’s clothing was made using velvet silk and other materials. They often used lace and gems to decorate the clothing they wore. The casual dress of queen’s could be either layered or without layers.
Peasants’ women wore dress-like tunics or kirtles. It was made of wood or undyed linen. Most women wore shirt beneath their tunic.
Women often covered their hair with either caps or veils. Head coverings for women changed from long veils to pointed caps to rolled bonnets.


Sumptuary laws
Laws that are restricted ordinary people in their expenditure. The sumptuary legislation of 1337 was designated to promote English garments and restrict the wearing of furs. English sumptuary legislation passed in included the following-
- Women were to be dressed according to the position of their fathers or husbands.
- Handicraftsmen’s and yeomen’s wives were not allowed to wear silk veils.
- Cloths of gold and purple silk were confined to women of the royal family.
These sumptuary laws distinguished social categories and made members of each class easily distinguished by their clothing.
