When was Sir Francis Bacon Born?
Sir Francis Bacon was born on 22nd January 1561 at York House in London. He was born as the youngest son to Sir Nicholas Bacon and his second wife Anne Bacon who was the daughter of an eminent humanist Anthony Cooke. Sir Nicholas Bacon was the Lord Keeper of the Seal of Elizabeth I.
Anne Bacon’s sister was the wife of William Cecil, 1st Baron Burghley making Francis his nephew. It is believed that Francis was tutored at home during the early years of his life because of his illness he was educated by John Walsall who was an Oxford graduate.
In 1573, Francis went to Trinity College, Cambridge when he was twelve years old. He stayed there for three years with his older brother Anthony under the guidance of Dr John Whitgift. A major portion of Francis Bacon’s education was in Latin and during his stay at the university, he met Queen Elizabeth for the first time.

She was very impressed by his intellect and would refer to Francis as ‘ the young Lord Keeper’. His education led him to believe that the way in which methods and results of science were carried out was full of flaws. He also opposed Aristotle’s philosophy.
In 1576, Francis along with his brother Anthony entered “de societate magistrorum” at Gray’s Inn and in the same year joined Sir Amias or Amyas Paulet on his trip to France.
Sir Paulet was the English ambassador in Paris. In France, Sir Francis gained a lot of valuable political information. After France, he also visited places like Blois, Poitiers, Italy, and Spain. While travelling he would learn languages, statecraft, civil law, and perform his diplomatic tasks.
In 1579, when Sir Francis was 18 years old, his father died and he had to return to England immediately. Sir Nicholas Bacon had saved a large amount of money to buy an estate for Francis but, before Sir Nicholas could execute his plans into action he died.
Facts About Sir Francis Bacon
Contents
The fact that Sir Francis was the youngest among the siblings, he was left with a barely one-fifth share of the money. This amount was not sufficient to survive and so Sir Francis borrowed money and was left with a debt to pay. In order to sustain and repay the money, Francis started living in Gray’s Inn and pursued the law as a profession.

He gave an application to his uncle, William Cecil stating his willingness to work in the court. This application was not accepted and he worked at the Inn for some time and after a couple of years, he was called at Bar in 1582. In 1584, Francis was just 23 years old and had entered the House of Commons.
During his struggling years, his rich relatives were of no help to him and it is even said that Queen Elizabeth did not trust him. However, after Queen’s death, James I of Scotland became the King. It was during the time of James I that Francis Bacon could build his proper career. Sir Francis was awarded a knighthood in 1603, became Baron Verulam in 1618 and 1st Viscount of St. Alban in 1621.
In 1586 he played a major role in the execution of Mary, Queen of Scots. Francis had three goals in his life- to uncover the truth, serve his country, and serve his church. He represented Melcombe in 1584 and Taunton in 1586 in parliament. Around 1591, Francis was the confidential adviser of Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, a favourite of the Queen.
Did Sir Francs Bacon have children?
No, Francis Bacon had no children and thus, the titles he was honoured with – Baron Verulam and Viscount St. Albans – died with his death.
What is Sir Francis Bacon known for?
Sir Francis Bacon, a Renaissance statesman and philosopher, was known for his promotion of scientific methods. He wanted to create a new outline for science and focussed on empirical scientific methods i.e. methods that could be backed by tangible proofs.
Bacon’s methods emphasised on experimentation and analysis. It included the gathering of information/data, analysing them and experimenting with them to deduce the truth of nature.
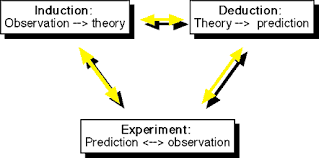
What did Sir Francis Bacon discover?
Francis Bacon discovered the scientific method that involved gathering data, analysing them and experimenting with them. He was against using arguments based on plain logic.
Francis Bacon’s Contributions
In 1596, Francis was made a Queen’s Counsel but missed the appointment of Master of the Rolls. In 1597, Francis published the first edition of his Essays along with Sacred Meditations and the Colors of Good and Evil. In 1608, Francis had entered upon the Clerkship of Star Chamber and received a considerable amount of income.
In 1613, he was appointed as the Attorney-General. Around 1621, Sir Francis had written the New Atlantis, a political romance. In the same year, he was charged with corruption in about 23 cases and the evidence against him was so strong that he did not make any attempts of defending the charges.
The Parliamentary Committee found him guilty and was required to pay a fine of $40,000 and to remain in the Tower during King’s pleasure. He was also not permitted to hold any office or sit in parliament. He very closely escaped from his titles being taken away from him.

How did Sir Francis Bacon die?
In 1626, Sir Francis returned to England. It was a snowy day when Francis was on his way home when he suddenly thought of doing some experiments with the properties of snow. It was during this experiment that Sir Francis caught pneumonia and eventually died at Arundel mansion outside London on 9th April 1626.
What is ‘Francis Bacon’ theory?
Sir Francis Bacon is called the Father of Empiricism. He believed in scientific knowledge that was based on experimentation and interaction rather than simple logical argumentation. He is, therefore, credited with developing the scientific method of study.
Francis Bacon’s Works
At the time of his death, he had a debt of $22,000 on him. Francis through his work provided for a method of developing philosophy. In De Augmentis Scientiarum(1623), Francis makes a distinction between the duty to community and duty to God. His famous work the Novum Organum was published in 1620.
The title of Francis Bacon’s work is a reference to Organon, Aristotle’s work. In Novum Organum, Francis talks about a system of logic far more superior than the old methods of syllogism. This work shows the beginning of the Baconian(scientific) method. It can be therefore said that Bacon was one of the most intellectual and powerful mind ever possessed by a man.

Francis Bacon Essays
Francis Bacon’s Essays is a collection of the essays written by the philosopher on a wide variety of subjects, such as mathematics, language, travel, history, truth, superstition, marriage and many more. He chose a vast range of topics in order to encourage people to think for deeply and analytically about everything.
Through his essays, Bacon not only provided a solid framework for the modern genre of the essay but also provided his readers with a standard code of living free from superstitions and wrong notions.
Francis Bacon’s Philosophy
In 1603, he was knighted during the reign of James I and he also endeavoured in writing Apology (defence) for his involvement and unfavourable action in the Essex case. Francis had penned many great works of philosophy in his lifetime and he led a full and intense life replete with loads of experiences.
Francis Bacon Quotes
- Knowledge is Power
- Some books are to be tasted, some to be swallowed and some few to be chewed and digested.
- The best part of beauty is that which no picture can express.
- Reading maketh a full man; conference a ready man; and writing an exact man.
- Truth is the daughter of time, not of authority.

