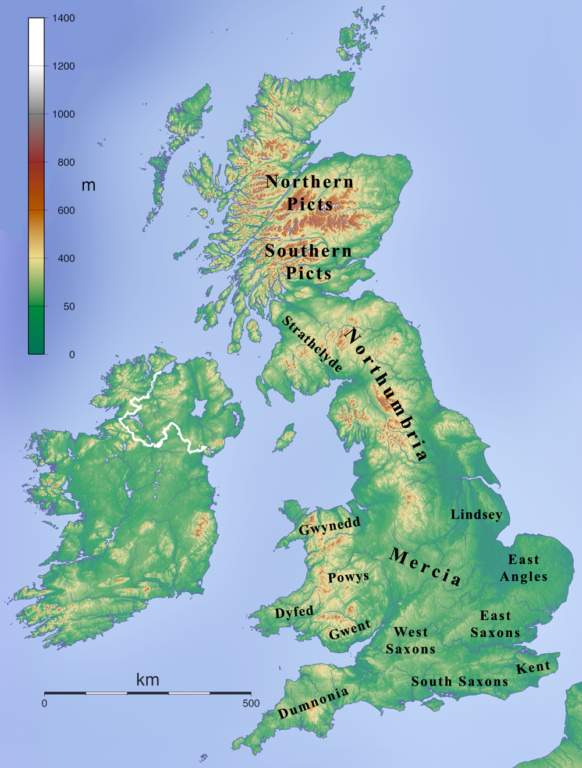
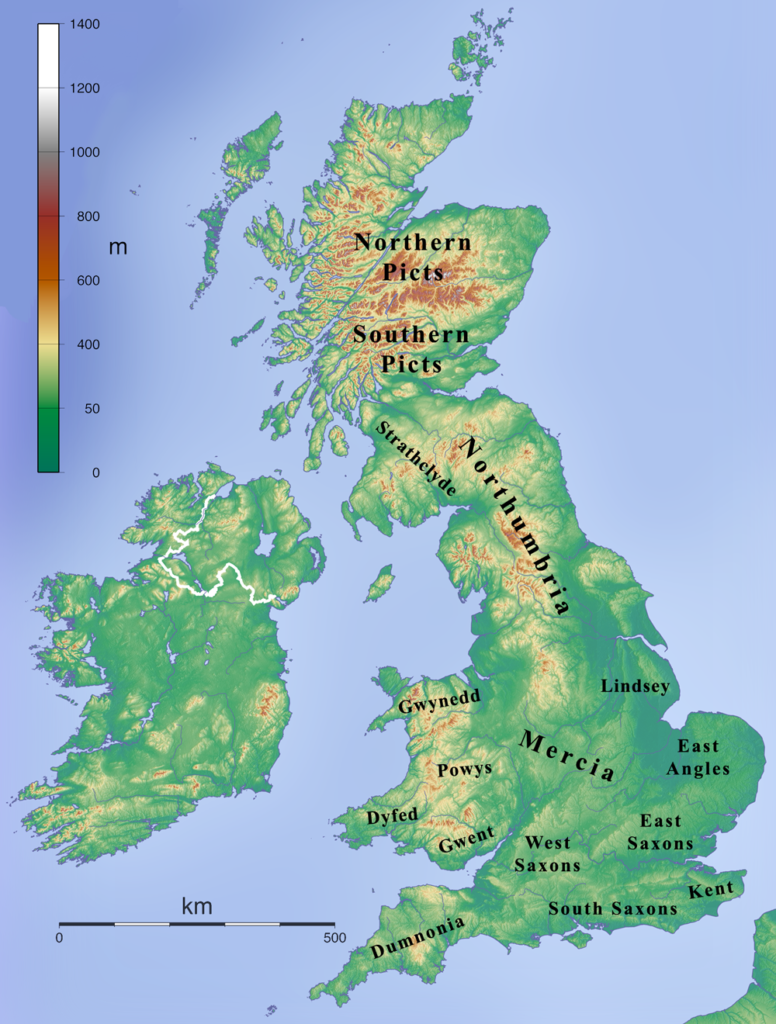
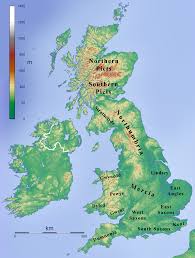
The Anglo-Saxon invasion broke up Britain into smaller parts called Kingdoms each ruled by a separate king or sub-king. These kingdoms were established during the late 5th century until the end of the Anglo-Saxon era in the 9th century due to the Norman conquest.
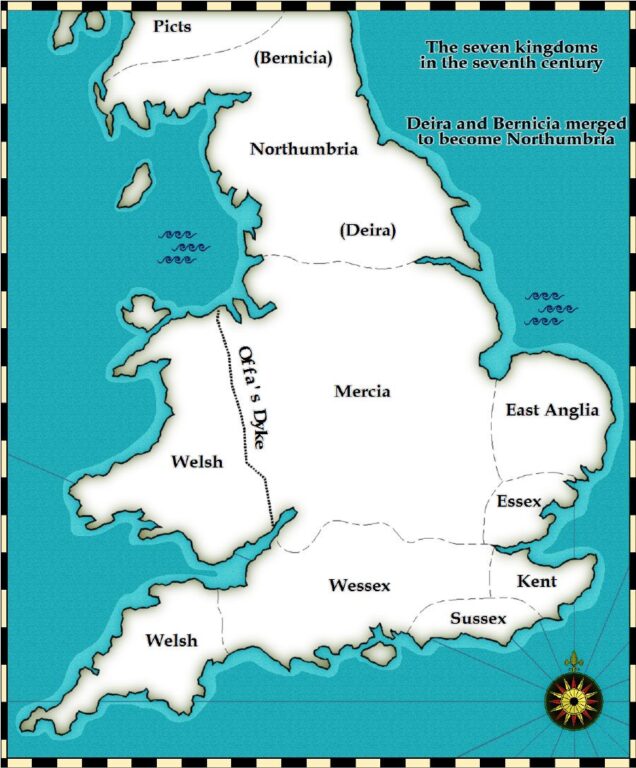
Anglo-Saxon Map: What all areas did they control?
Contents
What were the 7 Anglo-Saxon kingdoms?
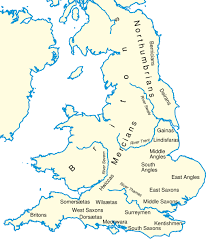
Heptarchy derived from the Greek words ‘seven’ and ‘rule’ was used to describe the 7 kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England. The kingdoms were namely Kent, East Anglia, Northumbria, Mercia, Essex, Wessex, and Sussex.
In the early 490 AD, Kings with greater holds of power were called ‘Bretwalda’. The first Bretwalda of Saxon kingdom was Aelle of Sussex in 490 AD. But it was not until the 9th century that Anglo-Saxon England recognized their first ever king Alfred the Great or King Alfred of Wessex.
Tha Anglo-Saxon map of Britain was similar to the current map of Britain in many ways, except the kingdoms that were there in the middle ages.
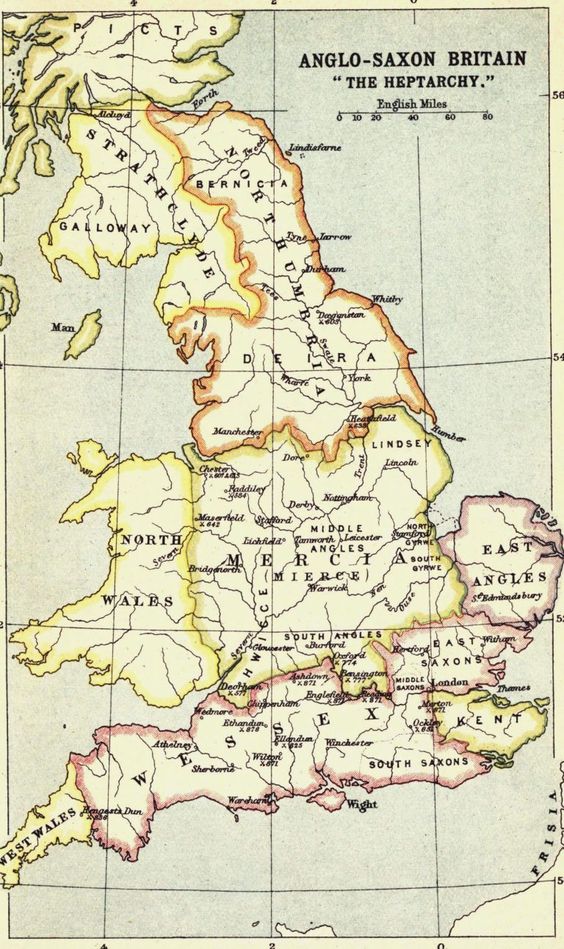
Heptarchy: 7 Anglo-Saxon Kingdoms
Kent
Kent was the first Anglo-Saxon Kingdom and was established in 449 AD. The first King to rule Kent was Hengist, prince of Angeln from 449 to 488 AD.
The people of Kent also known as Canti were originally German Jutes and Celtic Britons. They practised a custom called ‘gavelkind’ or partible inheritance which lasted till 1925.
By the end of the 6th century, Kent witnessed great success and emerged as one of the wealthiest kingdoms under the efficient leadership of King Ӕthelbert.
Ӕthelbert was a visionary and he was the first king to accept Christianity. He married Berth who was a Frankish Christian princess. During his reign, Christian missionaries introduced Roman alphabets and Latin languages and no doubt King Ӕthelbert was accepted as the Bretwalda until his death in 616.
The Canterbury was established by St Augustine and it remained a major intellectual centre for many decades.
East Anglia
East Anglia or the East Angles controlled countries of Norfolk and territories of South Angle Folk. King Rӕdwald was one of the most influential kings of East Anglia. The epic poem, Beowulf was developed here in East Anglia.
It was during the 7th century that a king of East Anglia discovered the Sutton Hoo Ship treasures which are now in modern-day Suffolk. The ruins of the 27-meter long ship were hoarded with textiles, weapons, armour, gold coins, ornaments, and symbols of Anglo-Saxon history.
Historians believed that the remains might have been of kings who lived nearby at Rendlesham who died between 617 and 631 AD. It was argued that it was probably king Rӕdwald who was buried in Sutton Hoo.
Anglo-Saxon map of East Anglia:
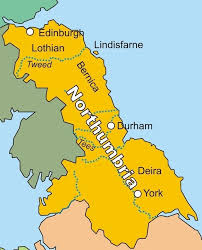
Northumbria
Northumbria was one of the most prominent kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England and had great contribution in the history and culture of the Anglo-Saxon community.
Lying in the North of the River Humber, Northumbria was originally formed by the coalition of two smaller kingdoms, the Bernicia and Deira.
Northumbria was the seat for many great scholars and artists. Venerable Bede was an eminent theologist and historian during that time and was rightfully called the ‘Father of English History’. He died at 735 AD.
The late 7th and early 8th centuries were considered to be the ‘Golden Age’ of Northumbria. It was during this time that Benedict Bishop who gave up his life as a warrior to become a monk founded the twin monasteries of Wearmouth and Jarrow in 674 in Northumbria. The monasteries achieved great significance but were later destroyed by the Danes in 860.
After the death of the last Northumbrian king Erik Bloodaxe in 954, the kingdom was taken over by King Edred of Wessex.
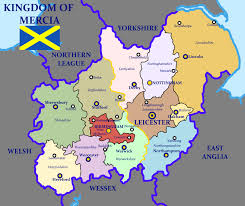
Mercia
Mercia emerged as one of the most powerful Anglo-Saxon Kingdoms during the 700s. It included parts of Northamptonshire, Huntingdonshire, Hertfordshire, Worcestershire, sub-kingdoms of Magonsets, South and Middle Angles, Hwiccas, Gainas, and many other smaller countries.
The first Mercian King was Penda and was a dominant ruler of the Mercian lands. It was during his reign, that Mercia evolved as a powerful Kingdom both in matters of wealth and military strength. A glimpse of the wealth could be found at Staffordshire which was the heart of the Mercian empire. Large collections of gold artefacts and military items were excavated at the Staffordshire Hoard near Lichfield in 5th July 2009.
Penda’s successor, his Christian son Wulfhere died in 675 and King Ӕthebald took over the kingdom in 716. After his death in 757, King Olfa succeeded the throne and established his power to the East of Anglia and Kent. Mercia was also a major trading centre and traded goods from different countries.
Essex-Kingdom of East Saxons
The East Saxons started settling in Essex from circa 500. It mainly comprised of the territories of Middlesex, Hertfordshire, Haemele, Vange, Denge, Ginges, Berecingas, Haeferingas, and Uppingas; London being its chief town. The Germanic Jutes tribe and Celtic Britons were the chief inhabitants of Essex.
The first king of Essex was Aescwine who ruled from 527 to 587 AD. From 664, Essex was jointly ruled under the jurisdiction of Mercia. In 825, King Egbert of Wessex defeated and took over Mercia in the Battle of Ellandon. Essex being a sub-kingdom of Mercia surrendered to Wessex.
King Egbert took over London and in 829 Essex lost its independence and finally merged with Wessex.
Wessex-Kingdom of West Saxons
The Kingdom of Wessex was founded in 519 circa by West Saxon chieftain Cerdic and his grandson Cynric in the upper Thames Valley. Wessex covered countries of Hampshire, Berkshire, Devon, Somerset, Dorset, and Wiltshire.
Wessex was in continuous conflict with its neighbouring kingdom Mercia until King Egbert of Wessex defeated King Beornwulf of Mercia in the Battle of Ellandune. Surrey, Sussex, and Essex surrendered and Edbert’s eldest son Ethelwulf was declared the sub-king of these 3 regions.
Beornwulf of Marcia wanted to reinstate himself to his Kingdom. The East Anglians sought the protection of King Egbert and Beornwulf was later defeated and killed. Wiglaf succeeded him who was later expelled from his kingdom by Egbert.
Egbert also took over Northern Northumbria and gained control all over England which earned him the title of Bretwalda.
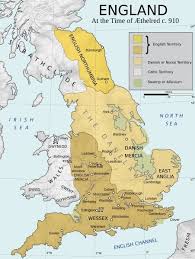
Where is current day Wessex?
The Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Wessex encompasses the regions of Hampshire, Isle of Wight, Dorset and Wiltshire today. The areas of the western half of Berkshire and eastern hilly regions of Somerset were also a part of the Wessex kingdom.
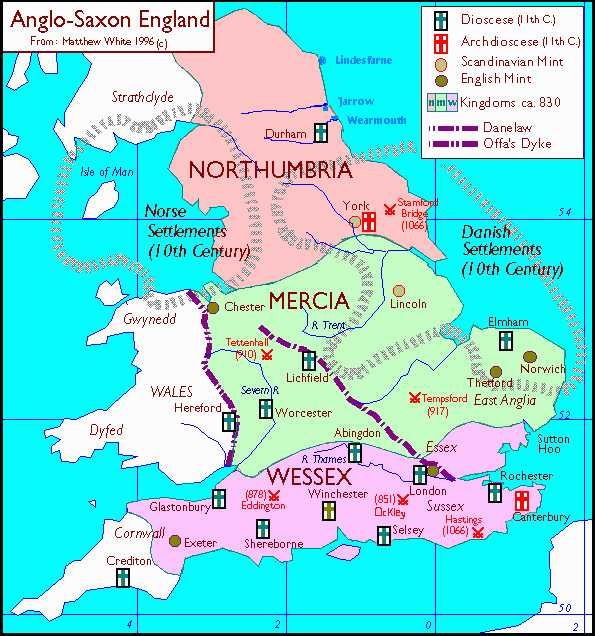
Sussex-Kingdom of South Saxons
A major part of the Sussex covered the territories of the Forest of Andred. The thick dense forest extended to an area of 120 miles and was a home for wild boars, wolves, and bears.
The first ruler of Sussex was King Ӕlle who invaded the region in 477 with his base at Pevensey. The invasion cost the lives of many Celtic Britons and the rest of the inhabitants were driven out of the region.
Sussex had joint rulers. The last rulers who ruled jointly were Atlfwald, Ealdwulf, and Oslac.